Architecture
The Art & Science of Designing and Constructing Buildings.
Arch
Arch, in architecture and civil engineering, a curved member that is used to span an opening and to support loads from above. The arch formed the basis for the evolution of the vault.
Beam
In building construction, a beam is a horizontal member spanning an opening and carrying a load that may be a brick or stone wall above the opening, in which case the beam is often called a lintel (see post-and-lintel system).
Brick
A brick is building material used to make walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Traditionally, the term brick referred to a unit composed of clay, but it is now used to denote rectangular units made of clay-bearing soil, sand, and lime, or concrete materials.
Building
1. A structure with a roof and walls, such as a house, school, store, or factory.
synonyms: structure, construction, edifice, erection, pile; More
2. The process or business of constructing something.
"the building of highways"
synonyms: construction, erection, putting up, raising, establishment, fabrication, production, assembly"a moratorium on the building of new power stations.
Ceiling
Ceiling, the overhead surface or surfaces covering a room, and the underside of a floor or a roof. Ceilings are often used to hide floor and roof construction.
Ceramic
Ceramics are a material often used in construction, made from a mixture of minerals, typically silica sand, with a clay binder and some impurities, and up to 30% water.
Color
the property possessed by an object of producing different sensations on the eye as a result of the way the object reflects or emits light.
Column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member.
Concrete
Architectural concrete refers to concrete that while providing an aesthetic finish to the building also serves a structural function. Decorative concrete typically refers to concrete flatwork or building elements such as panels, that while enhanced with texture or color, are not structural building members.
Construction
The building of something, typically a large structure.
"there was a skyscraper under construction"
* the building of large structures considered as an industry.
synonyms: building, erection, putting up, setting up, raising, establishment, assembly, manufacture, fabrication, forming, fashioning, contriving, creation, making"the construction of a new airport"
* the style or method used in the building of something.
"the mill is of brick construction"
Design
1. A plan or drawing produced to show the look and function or workings of a building, garment, or other object before it is built or made.
"he has just unveiled his design for the new museum"
synonyms: plan, blueprint, drawing, scale drawing, sketch, outline, map, plot, diagram, delineation, draft, depiction, representation, artist's impression, scheme, model, prototype, proposal"an architect submitted a design for the offices"
2. An arrangement of lines or shapes created to form a pattern or decoration.
"pottery with a lovely blue and white design"
synonyms:pattern, motif, device; More
Door
Door, barrier of wood, stone, metal, glass, paper, leaves, hides, or a combination of materials, installed to swing, fold, slide, or roll in order to close an opening to a room or building. ... Doors of rigid, permanent materials appeared simultaneously with monumental architecture.
Drawing
An architectural drawing or architect's drawing is a technical drawing of a building (or building project) that falls within the definition of architecture. ... Historically, drawings were made in ink on paper or a similar material, and any copies required had to be laboriously made by hand.
Electricity
Electricity. The term 'electricity' refers to the presence and flow of an electric charge. The most common form is that which is used to power appliances, machines and devices by the flow of electrons through conductors such as copper wires.
Fireplace
Fireplace, housing for an open fire inside a dwelling, used for heating and often for cooking. ... Early fireplaces were made of stone; later, brick became more widely used. A medieval discovery revived in modern times is that a thick masonry wall opposite the fireplace is capable of absorbing and re-radiating heat.
Fasteners
A fastener (US English) or fastening (UK English) is a hardware device that mechanically joins or affixes two or more objects together. In general, fasteners are used to create non-permanent joints; that is, joints that can be removed or dismantled without damaging the joining components.
Floor
A floor is the 'lower horizontal surface of any space in a building, including finishes that are laid as part of the permanent construction. ' A floor typically provides: Structural support for the contents of the room, its occupants, and the weight of the floor itself.
Foundation
A foundation is a lower portion of building structure that transfers its gravity loads to the earth. Foundations are generally broken into two categories: shallow foundations and deep foundations. A tall building must have a strong foundation if it is to stand for a long time.
Framing
Framing, in construction, is the fitting together of pieces to give a structure support and shape. Framing materials are usually wood, engineered wood, or structural steel.
Geometry
Architectural geometry is an area of research which combines applied geometry and architecture, which looks at the design, analysis and manufacture processes. It lies at the core of architectural design and strongly challenges contemporary practice, the so-called architectural practice of the digital age.
Glass
Architectural glass is glass that is used as a building material. It is most typically used as transparent glazing material in the building envelope, including windows in the external walls. Glass is also used for internal partitions and as an architectural feature.
Hardware
Door hardware (North American English) refers to any of the items that are attached to a door or a drawer to enhance its functionality or appearance.
Joinery
Joinery is a part of woodworking that involves joining together pieces of wood or lumber, to produce more complex items. Some wood joints employ fasteners, bindings, or adhesives, while others use only wood elements.
Light
1. The natural agent that stimulates sight and makes things visible.
"the light of the sun"
synonyms: illumination, brightness, luminescence, luminosity, shining, gleaming, gleam, brilliance, radiance, luster, glowing, glow, blaze, glare, dazzle; More
Masonry
Masonry (noun) is the building of structures from individual units, which are often laid in and bound together by mortar; the term masonry can also refer to the units themselves. The common materials of masonry construction are brick, building stone ...
Measurement
Measurement is the transformation of drawn information into descriptions and quantities, undertaken to value, cost, and price construction work, as well as enabling effective management.
Metal
Metals used for architectural purposes include lead, for water pipes, roofing, and windows; tin, formed into tinplate; zinc, copper and aluminium, in a range of applications including roofing and decoration; and iron, which has structural and other uses in the form of cast iron or wrought iron, or made into steel.
Moisture Protection
Thermal & Moisture Protection includes the materials used to seal the outside of the building against moisture, thermal, and air penetration, plus the associated insulation and accessories. ... Included are dampproofing, waterproofing, insulation, and roofing.
Order
Order, also called order of architecture, any of several styles of classical or Neoclassical architecture that are defined by the particular type of column and entablature they use as a basic unit. A column consists of a shaft together with its base and its capital.
Ornament
In architecture and decorative art, ornament is a decoration used to embellish parts of a building or object.
Paint
1. A colored substance which is spread over a surface and dries to leave a thin decorative or protective coating.
"a can of paint"
synonyms:coloring, colorant, tint, dye, stain, pigment, wash, color; varnish
Plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "render" commonly refers to external applications.
Plumbing
Plumbing, system of pipes and fixtures installed in a building for the distribution and use of potable (drinkable) water and the removal of waterborne wastes. It is usually distinguished from water and sewage systems that serve a group of buildings or a city.
Roof
A roof is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights; it provides protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of temperature, and wind. A roof is part of the building envelope.
Sitework
Sitework simply put, is part of a construction project that is not part of a building or house's physical structure. This usually includes grading, excavation, construction and installation of septic tanks and filtration systems, driveways and other utilities.
Stairs
Staircase, series, or flight, of steps between two floors. Traditionally, staircase is a term for stairs accompanied by walls, but contemporary usage includes the stairs alone.
Stone
Hard solid nonmetallic mineral matter of which rock is made, especially as a building material.
"the houses are built of stone"
Structure
The term 'structure' refers to anything that is constructed or built from different interrelated parts with a fixed location on the ground.
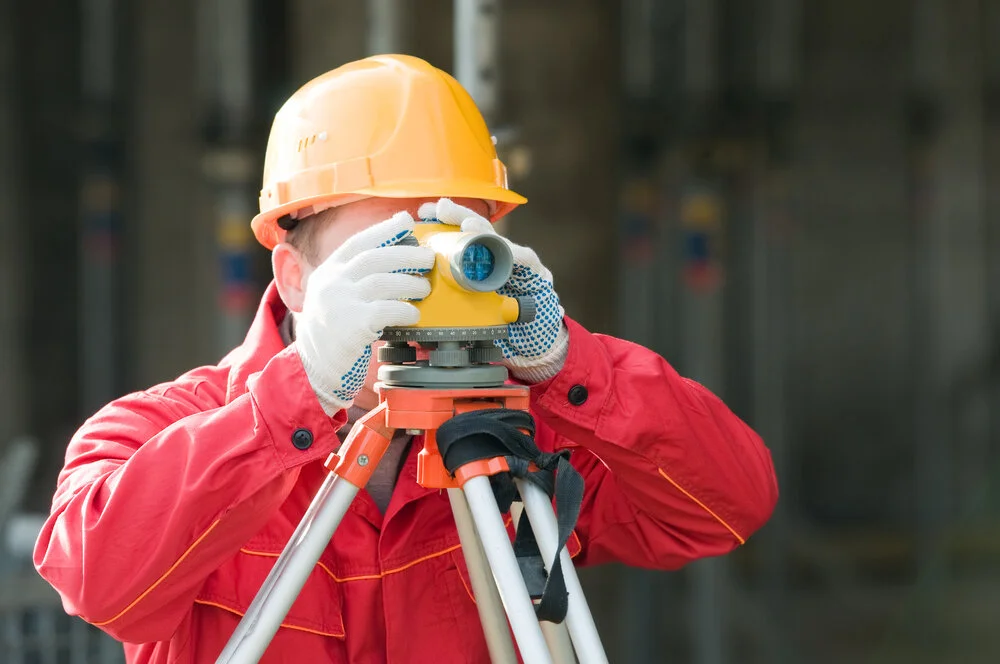
Survey
An act of surveying an area of land.
Sustainability
The ability to be maintained at a certain rate or level.
"the sustainability of economic growth"
Avoidance of the depletion of natural resources in order to maintain an ecological balance.
"the pursuit of global environmental sustainability"
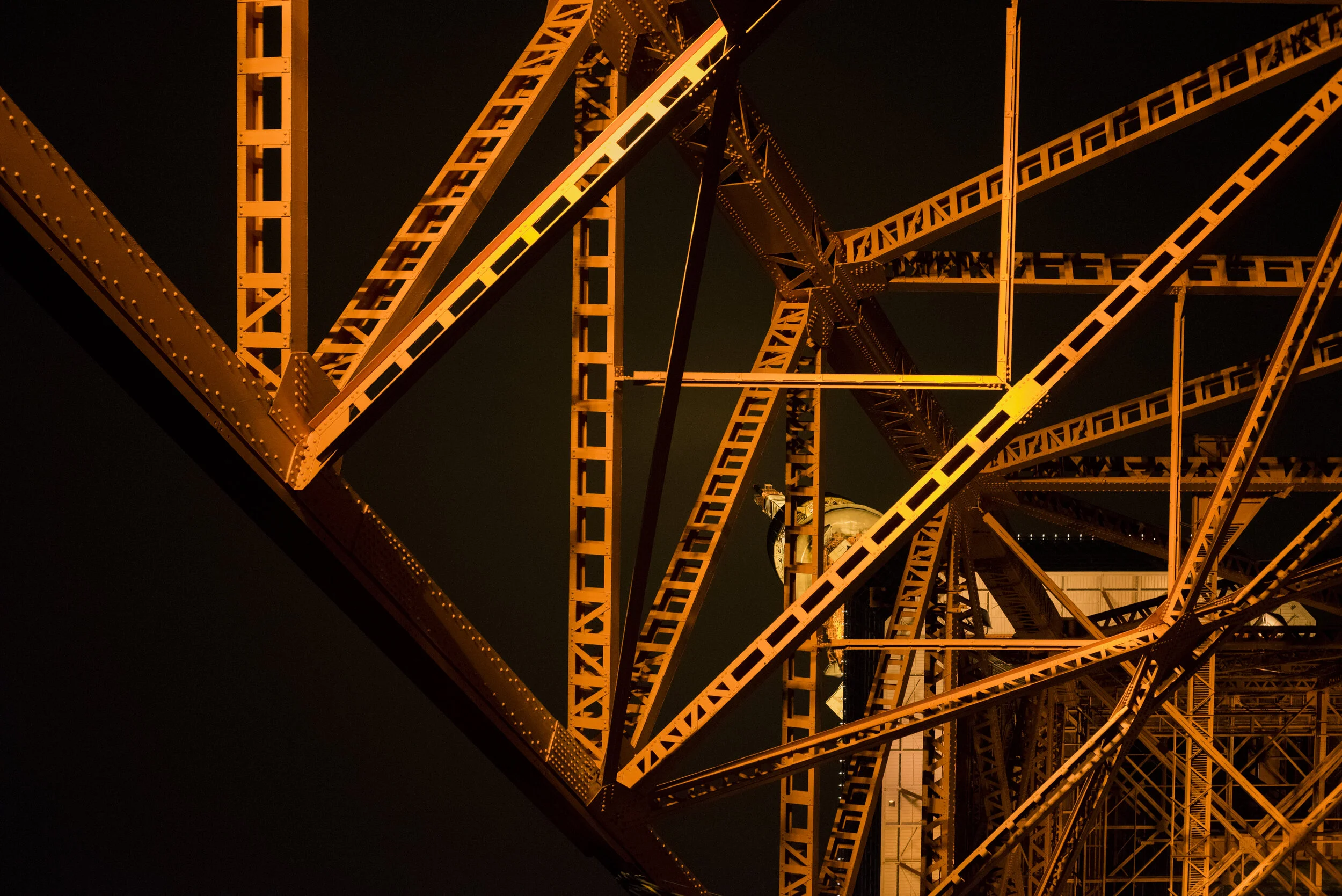
Truss
Truss, in architecture and engineering, a supporting structure or framework composed of beams, girders, or rods commonly of steel or wood lying in a single plane. A truss usually takes the form of a triangle or combination of triangles, since this design ensures the greatest rigidity.
Wall
Wall, structural element used to divide or enclose, and, in building construction, to form the periphery of a room or a building.
Window
Window. architecture. Window, opening in the wall of a building for the admission of light and air; windows are often arranged also for the purposes of architectural decoration.
Wood
Wood is a renewable material and uses less energy and resources to process compared to many other building materials. As wood has the capacity to store and remove CO2 from the atmosphere, it can have a particularly beneficial impact on the environment.